ABSTRACT
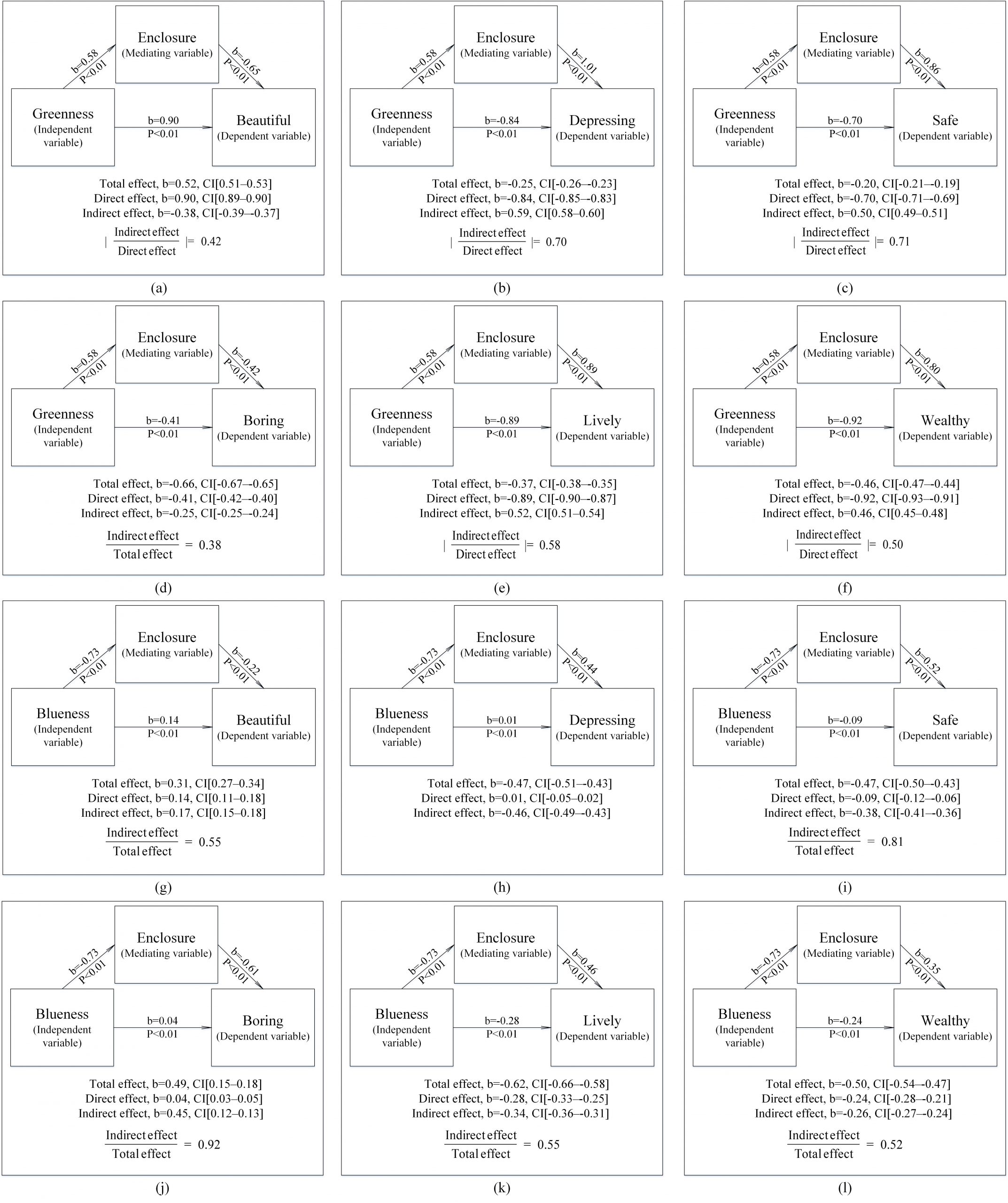
Although previous studies have assessed the relationships between visual space indicators and urban residents’ psychological perceptions, systematic research on the relationship between the urban visual space and residents’ psychological perceptions is still rare. The purpose of this study is to explore the correlation between the urban visual space and residents’ psychological perceptions, analyze the influence of visual space indicators on residents’ subjective perceptions, and focus on whether blue-green space is influenced by walkability, enclosure, openness, imageability, and traffic flow in the mechanism of its effect on urban residents’ psychology. In this study, the Fully Convolutional Network (FCN-8s) is used to segment the street view images of Wuhan. An urban perception data set is obtained by coupling the human-machine adversarial framework and the Random Forest algorithm. Based on the street view data, we design seven kinds of visual space indicators. We conduct multiple linear regression analysis on urban residents’ perceptions and the mediating effect analysis of blue-green space on residents’ psychology using the above five visual space indicators as mediator. The results show that there is a strong relationship between the urban visual space indicators and residents’ psychological perceptions, the visual space indicators such as greenness and enclosure have a strong influence on residents’ psychological perceptions and significant mediating effects of some visual space indicators occur in the process of blue-green space influencing residents’ psychology.
This study comprehensively analyzes the relationship and mechanism between visual space indicators and residents’ psychological perception, and makes forward-looking work to further explore the complex mechanisms between visual space and residents’ psychology.
Q.E.D.









